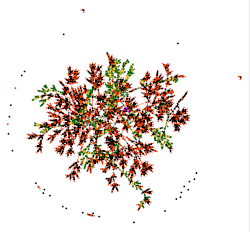
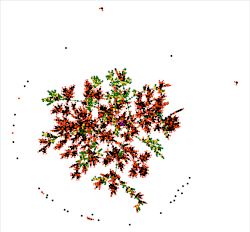
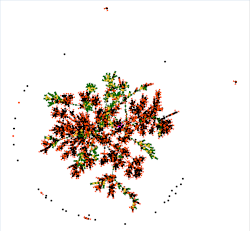
Graph (L)
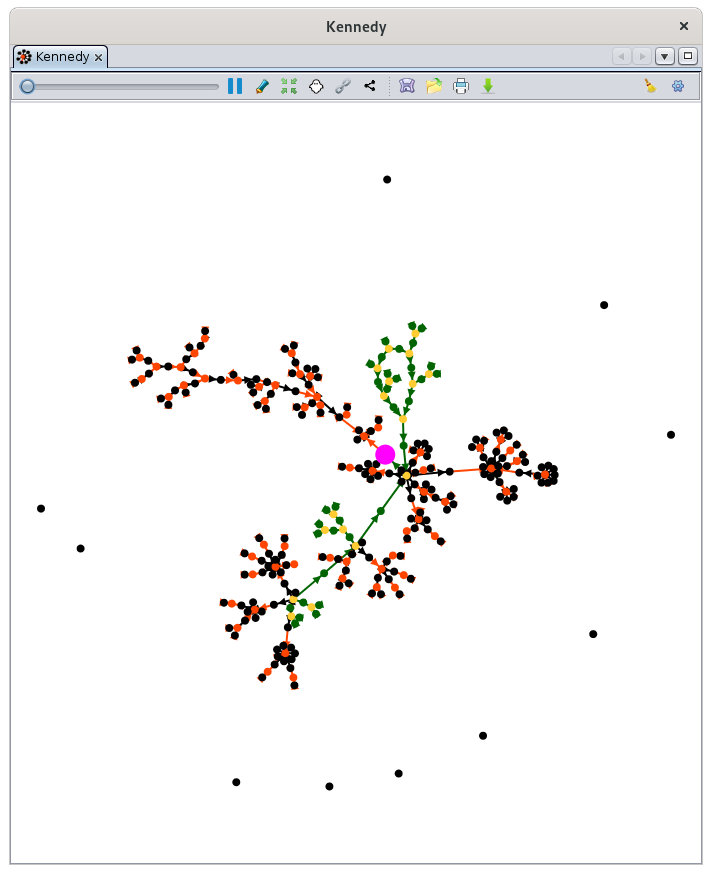
The Graph shows a view of your genealogy in the form of graphs,a graph, where all individuals are displayed only once, and are related to each other according to their genealogical relationships.
You can create your genealogy graphs as you wish. The shape of the graph can vary from one time to anotherthe next for the same genealogy, and also varies with each addition or deletion of individuals.
Description
This view displays the graph of your genealogy and a toolbar on the right allows you to make the settings you need.
The graph
The graph materializes all the individual and family entities of your genealogy as points. Other entities are not represented. These points are connected by arrows.
The points of individual and union
Individuals
The De Cujus individual, if it exists, is a point of larger size and pink color.
If Sosa numbers have been generated in the genealogy, one or more De Cujus individuals may exist and you will see several pink points. If no pink point is visible, it means that you have not yet generated any Sosa, or Sosa-d'Aboville numbers.
All other individuals are materialized by green points if they are in a Sosa lineage of a De Cujus, or by black points otherwise.
 |
 |
| Sosa individual | Non Sosa individual |
Each individual is displayed only once, even if he or she is implexed, i.e. if he or she is the common ancestor of a married couple.
Unions
All unions of Sosa individuals are materialized by yellow points, the other unions are orange points.
 |
 |
| union Sosa | Union non Sosa |
Each union is displayed only once.
The term union rather than family is used in the graph because it better explains the simple bond between two individuals than the term family which generally means a group of several people. Nevertheless, a union point does materialize a family entity.
In addition, the selected individual or selected union is shown as a blue point.
Arrows
Individuals and unions are connected by arrows of 3 possible colors according to three different meanings.
As the points represents individuals and unions, and because the arrows go down the timeline, the arrows can only represent the two different manners that links a individual and a union. Either the link is the "parent to union" or the link is "union to child". And there can be two variations : either in the Sosa lineage or not.
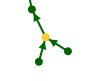
- The green arrows show the Sosa paths. They start from the ancestors at the top of your genealogy and go down to De Cujus, alternating between individuals and unions.
- Links alternate "parent to union" and "union to child", and they are Sosa. So the union is yellow. Example here :
-
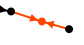
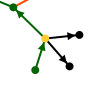
The orange and black arrows show the non Sosa paths:
-
The orange arrows are "parent to union" links, non sosa. So this is a couple and their union with no children:
-
-
- The black arrows are "union to non Sosa child" links.
 |
 |
| Non Sosa child from a Sosa union | Non Sosa child from a non Sosa union |
In addition, the arrows connecting the selected individual or family are blue lines.
Interpretations
Isolated Individuals, Isolated Unions, Isolated Trees
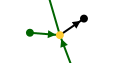
Isolated individuals are isolated black points. These are usually people in your genealogy who have witnessed events, or people you have captured and have not yet identified relationships for.
 Using the settings, you can view the relationship in the case of witnesses or associated persons. In such a case, a grey link appears with another individual or a union of the graph. You can then see the relationship of this witness to the person or events it relates to.
Using the settings, you can view the relationship in the case of witnesses or associated persons. In such a case, a grey link appears with another individual or a union of the graph. You can then see the relationship of this witness to the person or events it relates to.
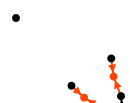 |
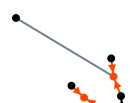 |
| Single individual at the top left |
In fact, it is a witness of a non Sosa wedding. |
If you find isolated unions, they are probably errors or family entities being entered. Here, two isolated unions next to an isolated individual :
You can finally find isolated trees of all sizes. Here, a small tree consisting of 3 unions and 4 individuals :
By the way, you can see here that even if the 3 unions are Family entities, we can hardly speak of "family" in the sense of a group of people made of parents and children. One can moreover detect an error there because the individual in black on the right is resulting child from 2 different unions in orange, which is not possible.
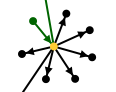
Large families
Large families are clusters with many black points around them. Here are two examples:
 |
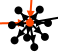 |
| Large Sosa family | Large non Sosa family |
Treetop Ancestors
The individuals at the top of your genealogy are the green points from which only an arrow starts. They are thus 1 or 2 green points (the parents of ancestors) that go to a yellow point (their union).
Here are a few examples:
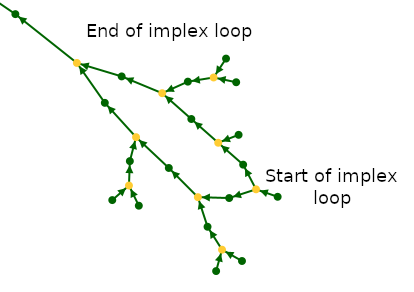
Implexes
Because of the construction of the green arrows, all the green loops you see are actually the result of the implexed ancestors at the top of these loops.
The implexes are in fact ancestors that appear several times in a classic family tree. In the graph, they appear only once.
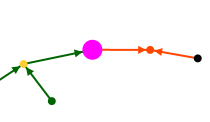
We therefore propose another definition of the implex: it is the union from which a consanguineous marriage will be born a few generations later. For each implex, we thus find ourselves with a loop in the graph, with the union of the implex ancestors at the top of the loop, and the consanguineous union at the base.
Here is an example from the Kennedy genealogy (the top of the loop reads in the direction of the arrows, it is at the bottom here) :
Case Study
Here is an example summarizing several of the interpretations above.
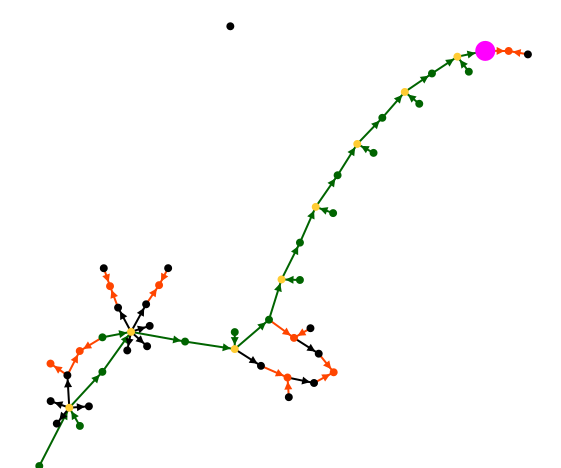
In the following example from the Bourbon genealogy, we see our De Cujus in pink who happens to be Louis XVI. To his right is his marriage with Marie-Antoinette whose ancestors are not shown.
If we go up the green arrows, the long branch is his ancestor line, where in each generation there is only one spouse. The other children are not shown if there were any.
We notice that this branch reaches a green individual, who is Louis XIV, from whom a first loop of implexe starts. It is Louis XIII who had as children Louis XIV and Philip I whose two descendants married each other.
We find a second loop of implexe upper in the ancestor line. It is surrounded by two large families: at the base of the implexe, that of Henri IV. At the top, that of Henri II.
We also locate an isolated individual who is not a witness, and probably shows that we have not finished grasping his relationship with the Bourbon.
The graph is an Ancestris invention and like you, we had never seen our genealogy in this form before. We are still discovering possible interpretations to this form of visualization. Let us know what you discover !
All colors are customizable. See the paragraph on customization below.
Toolbar
The graph toolbar is vertical on the right side of the window. It allows you to customize the appearance of the graph. Hover over each icon to display the tooltip explaining its function.
The toolbar presents the following tools:controls:
Zoom slider
This slider is used to adjust the zoom level of the graph display. Click/Drag to zoom in/out.
Pause automatic arrangement Button
At each opening of the graph view, the graph is built littleprogressively byuntil little.all the points are spread and visible. This button is used to stop/restart the construction of the graph.
Show / Hide names Button
Click here to show or hide the namesname of individual dotsindividuals and unionunions dots.at each point.
For thenames names,display, several choices are possible. TheyRefer are chosen into the CurrentConfigure View parameters.parameters.
CenteringCenter graph on click Button
It switches the mouse to "Centering"centering modemode" when it is pressed. It works in twothree steps:
- First you click on the button
sotothatgoit"centeringstays in the pressed position.mode". - Then you click on the
placepoint of the graph that you want to put in the center of thedisplay.display area. - You press the button again to stop the "centering mode".
Hide branches Button
It switches the mouse to "Hide"Hide modemode" when it is pressed. It works in twothree steps:
- First you click on the button to
keepgoittopressed."hide mode". - Then you click on an Individual point or a Union point. A menu appears asking you if you want to hide the ascending or descending part.
- You press the button again to stop the "centering mode"
After your choice, the graph adjusts accordingly.
The impact on the display can be quite logical: a branch disappears.
Sometimes the result can be quite curious: your tree can be separated into several pieces and individuals can be isolated.
You can re-display the hidden branches by clicking on the "Reset"Reset" button.
Show / Hide association links Button
This button allows to show or hide by grey links the relationships between isolated individuals and the graph.
Shortest path Button
It switches the mouse to "Shortest Path" mode when it is pressed.
It works in two steps.
- First you click on the first point
- Then you click on the second point
After your choice, the shortest path between the two points appears in blue and a window lists all the individuals between the two selected points.
Clicking on an individual displays it in the other views of Ancestris.
Save Button
The file will be saved with the name of the current tree and can only be opened with this Graph function.
Open Button
This button opens a previously saved graph. This will save you time when you reopen the graph by preventing it from rebuilding itself or to make sure you get back to a look you liked.
Print Button
This button allows you to print your graph. Ancestris will open it automatically with your svg file viewer (SVG is a vector image format.). It is from this software that you will be able to print it.
Export Button
Gephi is a free software for network analysis and visualization.
Reset button
This button resets the zoom, name display and hidden branches.
Configure view Button
This button allows you to change the display preferences of the graph. See the Customization section below for more details.
Usage
The purpose of this view is twofold:
- To present your complete genealogy visually in an esthetic form that you like
- Understand your genealogy and identify the parts that are sufficiently complete or conversely the parts that deserve further research.
Present your genealogy
As soon as the Graph view is launched, the graph is built progressively.
Generation of the graph
With many individuals, this can take a little time. If you have already built and saved a graph previously, simply click on the Pause button to stop the construction, then click on the Open button to fetch a previously generated graph.
The purpose of building the tree is to find the tree display which arranges all the branches so that each one is visible.
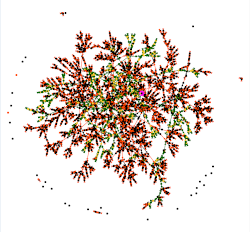
For example, here is the construction of the graph with 4200 individuals and 1300 families:
Modification
During construction, you can manipulate the graph or customize it if you wish.
Once the construction is complete, it is still possible to move points to better arrange the graph.
When you do this, it stretches the point corresponding to where you are moving it, and by inertia to maintain a sufficient distance between each point, it has the effect of a rubber band.
In the pause position, the points move one by one without the elastic effect.
If your graph suits you, remember to save it. It is difficult to find the exact same position several times.
Selection
Clicking on a point on the graph selects the individual or family in all other windows.
Conversely, a click on an individual or family in another window will refocus the graph on this entity, provided it is not in a hidden branch.
Analysis of your graph
This is the most interesting moment! You had never seen your tree like this, neither had we.
To analyze and understand your graph, you can proceed in different ways.
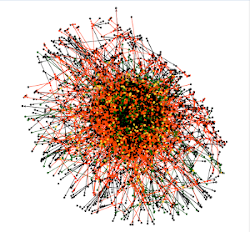
First there is a global macroscopic view, where you can see whether your tree is made up of a single Family Group or several. Each Family Group is in fact disjoint from the others.
In the example above, there is a single Family Group, with isolated individuals who are probably associations (witnesses, etc.). Here is a larger view to see better:
From De Cujus in pink, we see a few ascending lines in green/yellow, and many descendants or "cousins" in black/orange.
The longer the green lines, the more generations of ascendants.
We can also guess that there are a few implexe loops, but we will have to get closer to be sure.
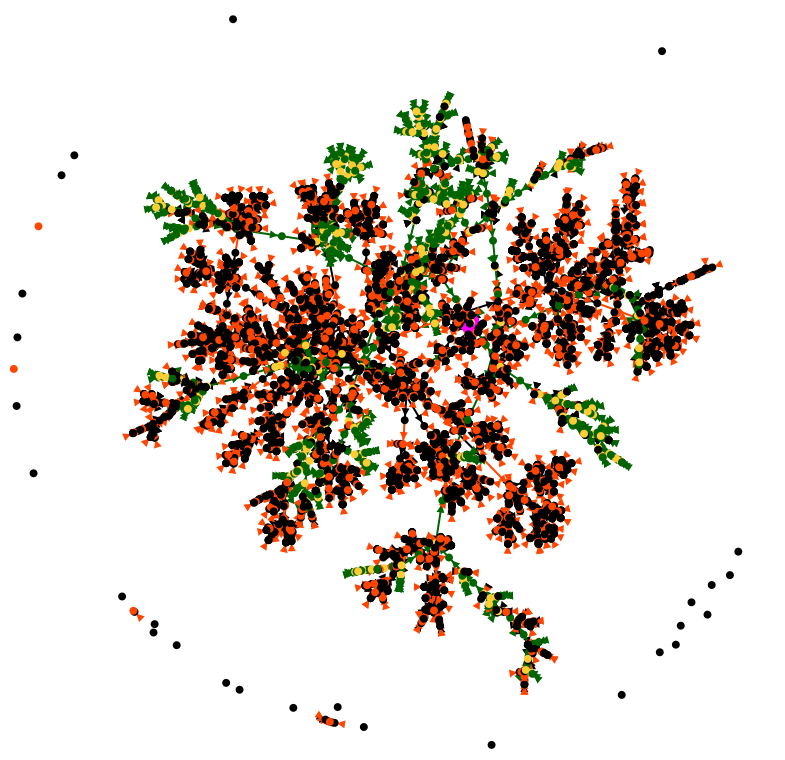
You can draw many more conclusions from this macro analysis, but let's move on to a more zoomed-in view. You have to realize that we have here about 5500 points in front of our eyes, the 4200 individuals and 1300 unions, and if you manage to see more, let us know!
By using the cursor button and the mouse to move the graph, we can get closer to De Cujus. When we are close enough, we can then display the names to know who we are talking about, using the toolbar button.
You can then hide the branches that might interfere with the view with the Hide Branches button or show them again with the Reset button.
Your analysis can then be done from branch to branch, successively from De Cujus to the most branches and to cousins or to ancestors.
To have the details of each point, just click on it and the other views will tell you which individual or family it is.
Shortest path
In the window that lists the individuals on the path, you can click on each of the names to make them appear in the other views of Ancestris and thus analyze this path in detail.
Update
The update is done in real time. Any change in your genealogy that leads to the creation or deletion of a family or individual, or the creation of a relationship between them, will update the graph.
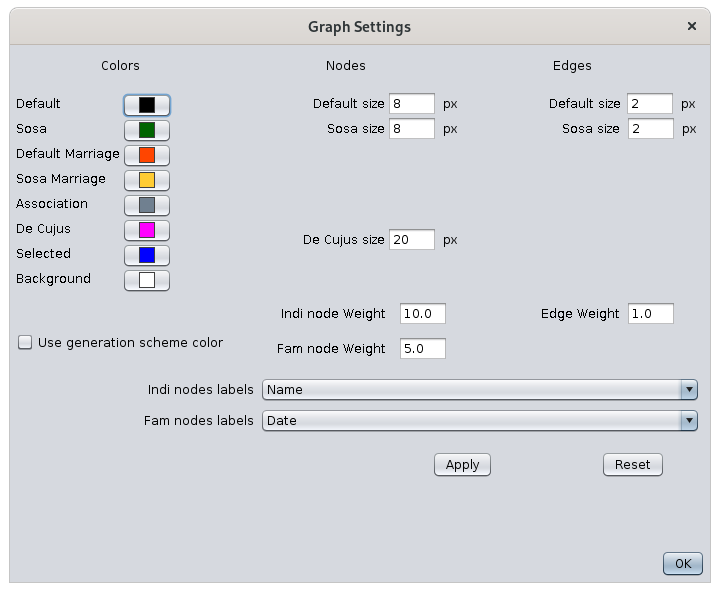
Customization
The customization of the graph is done with the parameters window that is obtained by clicking on the Current View Settings Button.
Colors
The left-hand column represents the current colors of the graph elements. By simply clicking on these buttons, you can change the color of the corresponding points and arrows, and the background color of the display.
Clicking on a color will open the color selection window. See the instructions for choosing a color in the Timeline view which has the same color.
A change of color in the settings window is immediately reflected in the graph and does not generate any modification of the graph structure.
Modification of the graph structure
It is possible to modify the apparent structure of the graph. These changes lead to the reconstruction of the graph, they do not immediately affect the graph. It is necessary to click on the Modify button.
The middle column allows you to indicate a new size of the points.
The right column allows you to indicate a new size of arrows.
The weights allow you to adjust the size of the points relative to the arrows.
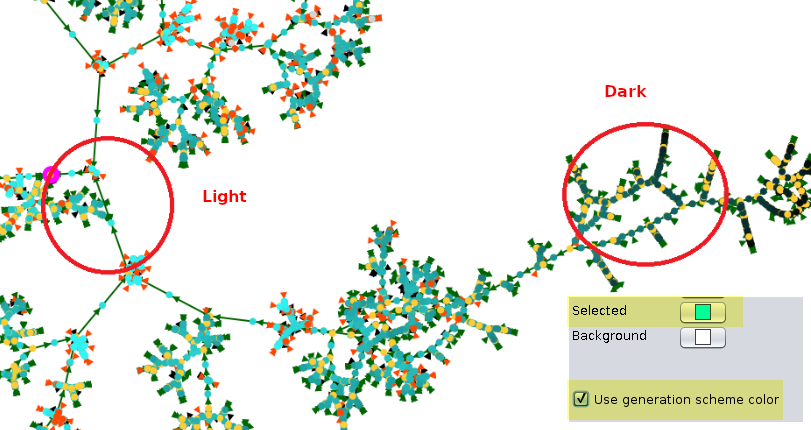
The checkbox Color gradient by generation allows you to distinguish the generations by color.
This function colors each generation with the same color gradient from the selection color to black. For the gradient to be clearly visible, it is necessary to approach light pastel colors, as in this example :
Modify Button
It modifies the display of the names according to the choices in the drop-down menus if the labels were already visible.
Default values Button
This button updates the structure of the graph to its default values.
OK Bouton
This Button closes the settings window. leaving the graph as it appears.
Tutorial
There is a tutorial on graphs in PDF format. You can download it here.